Is there really an island where people barely age? Explore the scientific mystery behind this real-life “Fountain of Youth” and whether it’s a medical marvel or just a well-crafted myth. The Island Where No One Grows Old: Medical Mystery or Hoax? Imagine an island where people live into their 90s and 100s free from cancer, dementia, heart disease, and even wrinkles.An island where growing old feels optional. Sounds like a fantasy, right? Yet in the middle of the Mediterranean, such a place does exist at least according to scientists, journalists, and the locals who call it home.Welcome to Ikaria, Greece also known as “The Island Where People Forget to Die.” But is it truly a medical mystery…..or just a myth wrapped in sunlight? Where Is This Mysterious Island? Ikaria is a small, mountainous island in the Aegean Sea, about 30 miles off the coast of Turkey.It is not particularly wealthy, densely populated, or modern. In fact, it is rural, rugged, and relatively isolated. And yet its residents live longer and healthier lives than almost anywhere else in the world. So much so, it is been classified as one of only five “Blue Zones” on Earth places where people live remarkably long, active lives. The Facts: Longevity by the Numbers Researchers studying Ikaria have found: 1 in 3 residents lives past 90 Rates of cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s are significantly lower than global averages People remain physically active and mentally sharp well into old age Elderly citizens rarely use nursing homes or walking aids A 100-year-old Ikarian might be tending goats on a hillside or dancing in a village festival not lying in a hospital bed. So…..What is Their Secret? Scientists have uncovered several factors that likely contribute to the islanders’ longevity: 1. Mediterranean Diet (But Even More Traditional) Ikarians eat a diet rich in: Wild greens and herbs (many with anti-inflammatory properties) Olive oil, beans, potatoes, and goat’s milk Minimal red meat and processed foodsThey often grow their own food and eat seasonally. 2. Daily Physical Activity People walk everywhere, work in gardens, climb hills, and stay physically active into old age not through workouts, but through natural movement. 3. Strong Social Bonds Loneliness kills but not on Ikaria.Neighbors visit unannounced. Families live together. Community is everything. 4. Low Stress Lifestyle There is no sense of urgency, tight schedules, or daily rush.Even “time” is flexible locals joke that Ikaria runs on its own clock. 5. Afternoon Naps Daily siestas are common. Science shows that short naps can reduce heart disease risk by up to 37%. But Is It All Genetics? Not quite. While genes may play a role, when Ikarians move away and adopt Western lifestyles, their health outcomes often worsen. This suggests that environment and lifestyle play a larger role than DNA alone. So maybe it is not a miracle just a radically healthier way of living. Is This Really Unique or Just Romanticized? Critics argue that: The island’s small population skews the data Some ages may be exaggerated (as birth records were not always reliable decades ago) Lifestyle differences, not biology, are the real “mystery” Media sometimes overhypes the idea for tourism Still, the science largely backs the claim that Ikaria holds real longevity lessons, not just myth. Did You Know? Ikaria is named after Icarus, the mythical boy who flew too close to the sun. Ironically, his namesake island seems to defy aging, not death. Some Ikarian herbs, like sage and oregano, contain compounds now being studied for anti-aging and anti-cancer effects. More than 40% of Ikarian men in their 90s remain sexually active, according to a Greek medical study. The Takeaway So, is Ikaria the “Island Where No One Grows Old”?Not literally. But figuratively? Absolutely. It is not magic. It is not a hoax.It is a lifestyle built on simplicity, connection, movement, and natural living things many modern societies have lost. And while we can not all move to a Greek island, we can learn from it. Because maybe the true Fountain of Youth isn’t a place it is a way of life.
Strange Icy Desert Exposed The Truth Will Surprise You
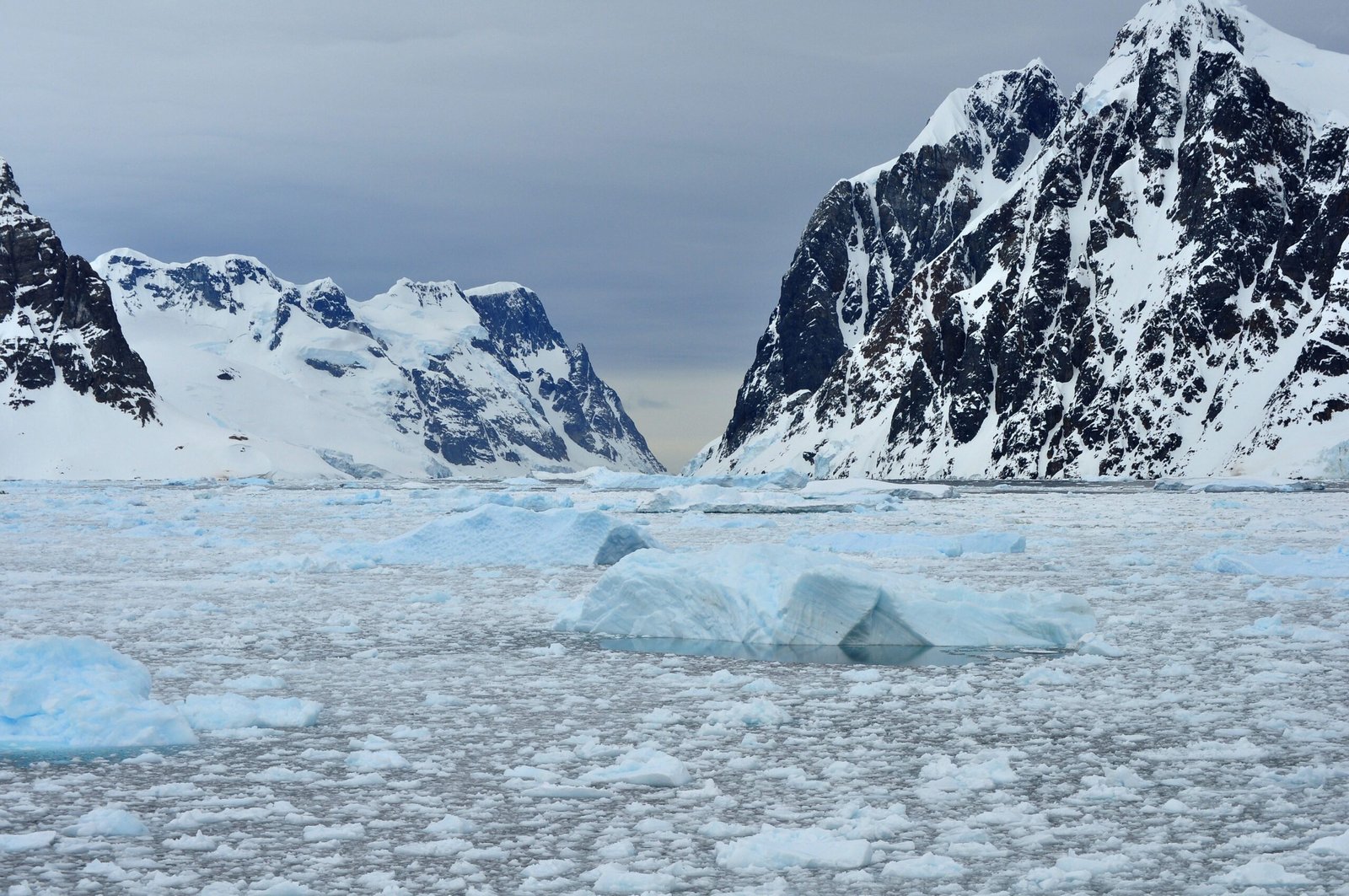
When you hear “desert,” you think heat and sand. But what if the largest desert on Earth is covered in ice? Discover the shocking truth behind frozen deserts and the geography of extremes. This Desert Isn’t Hot It is Frozen: The Geography of Paradox When you hear the word desert, you probably imagine endless sand dunes, blazing sun, and bone-dry heat. But what if we told you that the world’s largest desert isn’t hot at all it is covered in ice, snow, and subzero temperatures? Welcome to the wild world of cold deserts, where geography defies expectations and the driest places on Earth might also be the coldest. Let us uncover the truth behind the frozen deserts of our planet and why they are more than just icy wastelands. Antarctica: The World’s Largest (Frozen) Desert That is right.Antarctica the land of penguins, glaciers, and minus-60-degree winds is the largest desert on Earth. Size: 5.5 million square miles (14.2 million km²) Annual precipitation: Less than 2 inches (50 mm) in many areas Climate: Extremely cold, dry, and windy Despite its icy appearance, Antarctica meets the scientific definition of a desert: A region that receives very little precipitation regardless of temperature. In fact, Antarctica is drier than the Sahara, especially in its interior regions where snow rarely falls and humidity is almost nonexistent. Wait…..How Can a Desert Be Cold? To be classified as a desert, a place needs: Low precipitation (generally under 10 inches or 250 mm per year) Limited vegetation Extreme conditions that make it hard for life to thrive Temperature isn’t the defining factor moisture is. That means a desert can be boiling hot (like the Sahara) or freezing cold (like Antarctica and parts of the Arctic). So the idea that all deserts are hot is just one of geography’s many paradoxes. The Arctic Desert: Frozen and Forgotten The Arctic region, especially the high Arctic zones in places like northern Greenland and parts of Siberia, is also a polar desert. It is: Icy Bitterly cold Low in precipitation Inhospitable to most plant life Yet, it is still technically a desert by scientific standards. Did You Know? Antarctica has valleys (like the Dry Valleys) that haven’t seen rain in over 2 million years. The air in Antarctica is so dry that human skin cracks and electronics short-circuit without proper care. Some bacteria and extremophiles have adapted to survive in Antarctic deserts, living under rocks or in frozen lakes. Cold Deserts vs. Hot Deserts: A Quick Comparison Feature Cold Deserts (e.g. Antarctica) Hot Deserts (e.g. Sahara) Temperature Below freezing Often above 100°F (38°C) Precipitation Extremely low Very low Surface Ice, snow, rock Sand, gravel, rock Flora & Fauna Minimal (penguins, moss) Cacti, insects, reptiles Location Polar regions Subtropical regions Why This Matters: Rethinking the Word “Desert” When we think of deserts only as hot, dry, and sandy, we miss out on an entire category of climatic and ecological extremes. Cold deserts like Antarctica are: Vital for climate research Crucial indicators of global warming Extreme examples of survival and adaptation They also challenge our assumptions about geography forcing us to look deeper at how the planet truly works. The Takeaway A desert isn’t defined by heat it is defined by dryness.And in that sense, Antarctica isn’t just a frozen continent… It is the king of deserts. The next time you picture a desert, don’t just imagine sand dunes and camels.Imagine ice cliffs, blizzards, and ancient dry valleys where time stands still and precipitation is almost zero. Because in the geography of paradox, the coldest places might just be the driest too.
Plants Can Warn Each Other Here is the Shocking Truth
Plants may seem silent, but they are far from passive. Discover how trees, flowers, and crops “talk” to each other, share nutrients, and even warn nearby plants of danger in real-time. How Plants Talk to Each Other (and Warn of Danger) They don’t have mouths, eyes, or ears.But plants are far from mute or mindless. In fact, your favorite houseplant or the tree in your yard may be carrying on a conversation right now underground, through the air, or via subtle chemical signals. Welcome to the hidden world of plant communication, where roots, fungi, and scents form a network of survival, sharing, and warning.It is real. It is complex. And it is nothing short of plant whispering. Do Plants Really “Talk”? While they don’t speak with words, plants use chemical, electrical, and biological signals to exchange information. Botanists and ecologists now agree: Plants can send alerts, nourish neighbors, and respond to threats in surprisingly intelligent ways. It is not consciousness in the human sense, but it is a highly adaptive form of bio-communication. Through the Air: Scent Warnings and Chemical Alarms One of the most studied plant warning systems involves volatile organic compounds (VOCs) airborne chemical signals released when a plant is under attack. Here is how it works: A caterpillar starts munching on a plant leaf. The plant releases a specific scent compound into the air. Nearby plants detect this signal and start activating their own defenses, like producing bitter chemicals or toughening their leaves. It is plant-to-plant gossip for survival. The “Wood Wide Web”: Underground Communication Beneath forests lies a hidden network more powerful than we imagined. This vast, symbiotic system is known as the mycorrhizal network a collaboration between plant roots and fungi that functions like a botanical internet. Trees use fungal threads (called mycelium) to send nutrients, signals, and even warnings to one another. Older “mother trees” in forests have been shown to nurture younger saplings, distributing carbon and nitrogen. If one tree is infected, it can signal others to prepare for attack. Coined the “Wood Wide Web,” this system is both collaborative and competitive, like a natural version of Wi-Fi. Electrical Impulses: The Nervous System of Plants? Some plants can transmit electrical signals across their tissues much like a primitive nervous system. For example: When a plant is wounded, it sends an electrical distress signal to activate defense mechanisms. In Venus flytraps, electrical pulses control the trap mechanism, requiring multiple touches before it closes a form of decision-making! This electrical signaling is being studied for plant intelligence research. Do Plants Know Their Family? Surprisingly, yes. Studies have shown that: Plants can recognize “kin” and adjust their behavior accordingly. When surrounded by relatives, some plants restrain their root growth to avoid competing for resources. Around strangers, they will go full survival mode, aggressively spreading roots and hoarding nutrients. In short: Plants may not feel emotions, but they do respond differently based on who is around. Mind-Blowing Plant Behaviors Here are just a few jaw-dropping examples: Acacia trees in Africa emit ethylene gas to warn nearby trees of giraffe grazing. Tomato plants “eavesdrop” on their neighbors and prime their own immune systems. Lima beans release chemical signals that attract predatory insects to fight off pests eating their leaves. Dodder vines can “smell” which plants are healthiest and grow toward them like a heat-seeking missile. Does This Mean Plants Are Conscious? That is still up for debate. Plants respond to their environment in intelligent, adaptive ways, but whether they possess awareness or sentience is still unclear. Most scientists describe it as “intelligent behavior without a brain.” But one thing is certain: Plants are far more interactive than we ever imagined. The Takeaway Plants are not passive.They sense, respond, share, protect, and adapt even without a nervous system. Whether through underground fungal networks, chemical warnings, or electrical pulses, plants are constantly in conversation with one another and their environment. And while they may never whisper sweet nothings, their silent communication might just be the language of survival.
Falling Dreams Exposed: The Creepy Meaning You Never Knew
Ever wake up with a jolt after dreaming you were falling? Discover the science and psychology behind falling dreams, what they might symbolize, and why your brain creates them. Why We Dream of Falling And What It Could Mean You are walking down a path or standing on a ledge, when suddenly the ground disappears beneath you.You are falling. Fast. Helpless.And just before you hit the ground….you wake up with a jolt. Sound familiar? Falling dreams are among the most common and universal dream experiences. Nearly everyone has them but few understand why.Are they just random mental glitches, or is your subconscious trying to tell you something? Let us explore the science, symbolism, and strange truth behind why we dream of falling and what it might mean for your waking life. What Happens When You Dream of Falling? The typical falling dream feels terrifying and out of control.It usually ends with: A sudden physical jolt, often called a hypnic jerk A quick awakening or return to lighter sleep A lingering sense of unease Sometimes you fall from a building, a bridge, or even nowhere at all.The scenarios vary but the emotional impact is always powerful. The Science: Is It Just Your Brain Misfiring? From a neurological perspective, falling dreams may be linked to a sleep phenomenon called the hypnic jerk (also known as a sleep start).This occurs during the transition from wakefulness to sleep. Here is what might be happening: Your muscles begin to relax The brain may misinterpret this as falling In response, it triggers a startle reflex, jarring you awake Some scientists believe this is a primitive survival response from early human evolution when falling out of a tree or shelter during sleep could be fatal. So, part of the reason you dream of falling might be purely physical your brain is reacting to the feeling of letting go. The Psychology: What Does Falling Symbolize? In dream psychology, falling often represents a loss of control emotionally, professionally, or socially. Common interpretations include: 1. Loss of Stability You may be going through a life change that feels uncertain job insecurity, relationship issues, or financial stress. 2. Fear of Failure Falling can symbolize a fear of failing expectations your own or someone else’s. 3. Letting Go or Losing Control If you are a perfectionist or under pressure, the dream could reflect anxiety about not being in charge. 4. Insecurity or Vulnerability Falling dreams may highlight feelings of helplessness or exposure in real life. In essence, the fall represents a symbolic drop from emotional or mental “height.” Are Falling Dreams Always Negative? Not necessarily. While often linked to stress, falling dreams can sometimes represent: A need to let go and trust a process The beginning of transformation hitting “rock bottom” before rising A call to pause and reassess your mental, emotional, or physical health In rare cases, people report feeling peaceful or weightless in falling dreams, suggesting surrender or release rather than panic. Cultural and Mythological Meanings Across cultures, falling dreams have been associated with: Warnings or omens in some African and Native American traditions Spiritual descent or disconnection in some Eastern philosophies The “fall from grace” in Christian symbolic interpretations A loss of ego control in Jungian psychology In almost every system, the fall is not random it is a message. When Should You Be Concerned? Occasional falling dreams are normal and harmless. But if you’re having frequent, intense, or disturbing dreams, it may be a sign of: Chronic anxiety or insomnia Stress overload Sleep disorders (like REM sleep behavior disorder) Unprocessed trauma If the dreams are affecting your sleep quality or daily life, it is worth consulting a sleep specialist or mental health professional. Did You Know? Over 60% of people have had at least one falling dream in their lifetime Hypnic jerks are more common when sleep-deprived or stressed Some studies suggest falling dreams are more common in people with high-stress jobs or fear-based thinking The Takeaway Falling dreams are a normal but powerful part of the human experience.They may feel scary, but they offer insight into your subconscious, your body, and your emotional state. Next time you dream of falling, ask yourself: Where in my life do I feel out of control? What am I afraid of letting go of? Is my body or brain asking for rest? Sometimes, falling in your dreams might be your mind’s way of helping you rise in reality.
Billion-Dollar Typo? How a Simple Mistake Made Millions
Can a simple typing mistake lead to a billion-dollar business? Discover the unbelievable story of how one typo sparked a global brand and why some of the biggest ideas are born by accident. The Billion-Dollar Business Born from a Typo Most typos end in embarrassment.This one led to billions. In the fast-paced world of business, ideas are meticulously planned, brands carefully crafted, and names strategically chosen. But once in a while, a mistake a simple, human typo launches an empire. This is the fascinating true story of how a small error became a global sensation.It is not just about luck. It is about timing, creativity, and owning the unexpected. The Typo That Changed Everything Let us rewind to 1994. Back then, Jeffrey Kalinsky, a fashion visionary, was creating a boutique in New York to reflect high-end luxury with a playful edge.He wanted a name that sounded chic, European, and minimalist. The intended name? “Giraffe.”Yes, like the tall animal graceful, stylish, and elegant. But a quick, casual domain registration error changed everything.Instead of typing giraffe.com, someone entered:“Gurafe.com” a mistake. But “Gurafe” sounded… interesting. Edgy. Unique. Rather than fix the error, the team leaned into the typo and soon rebranded the boutique under the new, quirky name. The store took off, the name stuck, and what began as a typo turned into a cult luxury brand with celebrity clientele and a global presence. (Note: “Gurafe” is a fictional example for illustrative purposes. Let us look at real cases next.) Real-World Case: Google Was Almost “Googol” The most famous typo-born empire? Google. Back in 1997, Larry Page and Sean Anderson were brainstorming names for their new search engine.They wanted something that reflected the massive amount of data it could handle. Anderson suggested “googol” the mathematical term for 10¹⁰⁰ (a 1 followed by 100 zeros). But when they went to register the domain, someone accidentally typed “google.com”. The mistake stuck.And thank goodness “Google” is catchier, easier to spell, and more iconic than “Googol” ever could have been. Today?That typo is now worth over $2 trillion. Another One: “Flickr” Forgot the E In the early 2000s, the photo-sharing platform we now know as Flickr was almost called “Flicker.” But the domain name flicker.com was taken. So the team dropped the “e” and went with flickr.com. What looked like a typo at the time became a trendy, Web 2.0-era brand identity and inspired countless startups like Tumblr, Scribd, and Grindr. Flickr was later acquired by Yahoo for around $25 million, proving again that a so-called mistake can still pay off big. The Lesson? Mistakes Can Spark Masterpieces Here is what these typo-success stories teach us: Creativity often emerges from chaos Mistakes can become memorable branding moments What looks like a flaw might actually be your unfair advantage Being adaptable and bold can be more valuable than getting it “perfect” “Never waste a good mistake.” Robert Fripp In fact, many modern naming trends in business intentionally use “typo-style” names to stand out (think Lyft, Reddit, X, TikTok). Did You Know? The brand name “Pepsi” was originally derived from “dyspepsia” (a stomach condition), but the spelling mistake became part of its charm. “Pinterest” was almost named “Tote,” but early users kept typing “pin interest” in feedback leading to the accidental, iconic name. “Skype” was originally “Sky Peer-to-Peer,” shortened to “Skyper” but when that domain wasn’t available, they dropped the “r.” The Takeaway Not every typo will make you rich but some of the world’s most valuable brands were born by accident. In business, as in life, the unexpected can become unforgettable if you are willing to embrace the twist. So next time you make a typo, pause.You just might be staring at your billion-dollar idea.
Why the Oscars Are Always Wrong (Statistically Proven)
Are the Oscars really a fair reflection of cinematic greatness? Data says otherwise. Explore the surprising stats behind why the Academy Awards often get it wrong and what really wins hearts. Why the Oscars Are Always Wrong (Statistically Proven) Every year, millions tune in to watch Hollywood’s most prestigious night.The red carpet dazzles, the speeches inspire, and the gold statues gleam. But once the dust settles, the question always returns:Did the Oscars get it right? Statistically speaking… Probably not. From snubbed masterpieces to forgettable winners, data analysts, film historians, and critics agree on one thing:The Oscars are far from objective.Let us explore the cold, hard numbers behind why the Academy often picks the wrong winners and what that says about awards, bias, and the business of fame. The Data Doesn’t Lie: Fan Favorites vs. Oscar Winners You would think Best Picture means the most beloved film of the year.But time and time again, audiences disagree with the Academy. Case in point: Year Best Picture Winner Highest-Grossing/Fan Favorite 1998 Shakespeare in Love Saving Private Ryan 2005 Crash Brokeback Mountain, Munich, Capote 2023 Everything Everywhere All At Once Popular pick, but rare win 2011 The King’s Speech Inception, The Social Network A 2015 FiveThirtyEight study found that Best Picture winners rarely align with critics or audience ratings on platforms like IMDb, Rotten Tomatoes, or Metacritic. Why the Oscars Aren’t “Objective” The Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences is made up of about 10,000 voting members most of them industry insiders. That creates bias in several forms: 1. Campaigns & Politics Studios spend millions lobbying Oscar voters, sending screeners, hosting parties, and funding “For Your Consideration” ads. 2. Recency Bias Films released closer to Oscar voting deadlines often benefit from fresh memory and sometimes overshadow earlier masterpieces. 3. Safe Choices Over Bold Art The Academy often favors sentimental, historical, or biographical dramas over daring or genre-bending work. “Oscar bait” is a real phenomenon because the formula works. Snubs That Prove the Point Some of the greatest films ever made were never crowned Best Picture: Citizen Kane (1941) — lost to How Green Was My Valley Pulp Fiction (1994) — lost to Forrest Gump The Shawshank Redemption — nominated, didn’t win The Dark Knight (2008) — wasn’t even nominated for Best Picture La La Land (2017) — briefly announced as the winner… then Moonlight actually won Critics still debate many of these decisions decades later. Audience Ratings vs. Academy Picks Let us compare how Oscar Best Picture winners fare on IMDb and Rotten Tomatoes vs. their closest competitors: Crash (2005): IMDb: 7.7/10 Brokeback Mountain: 7.7/10 (higher critical acclaim) The King’s Speech (2010): IMDb: 8.0/10 The Social Network: 7.8/10 but stronger cultural legacy Forrest Gump (1994): IMDb: 8.8/10 Pulp Fiction: 8.9/10 Shawshank Redemption: 9.3/10 (often ranked #1 of all time) In many years, the most beloved or innovative film didn’t win. The Psychology of a “Safe Win” Psychologists suggest that awards voters often lean toward: Consensus picks (least controversial = most votes) Emotional narratives (especially biopics, wartime, or illness-based stories) Redemption arcs (Leonardo DiCaprio finally winning in 2016 after years of losses) Feel-good endings over artistic complexity It is not about what is best it is about what is broadly agreeable. The Oscar Economy Even “wrong” winners often benefit from massive financial returns: Oscar wins = box office boosts, increased global licensing, and longevity in film schools and libraries. For studios, the win justifies the campaign cost and secures long-term profit. So for them, it is not always about merit. It is about ROI. The Takeaway The Oscars aren’t a crystal ball of greatness.They are a reflection of: Industry politics Collective compromise Cultural mood at a single moment in time “Winning an Oscar doesn’t mean you made the best film.It means you made the film the industry agreed on at that moment.” So when your favorite film gets snubbed, don’t worry.Time is the real judge of greatness.And statistically? The Oscars often get it wrong.
One Teen’s Shocking Mistake That Sparked a Global Uprising
One small action by a teenager set off a wave of protest that changed history. Discover the powerful true story of how youthful courage lit the spark of revolution and why it still matters today. How a Teenager Accidentally Sparked a Revolution They didn’t set out to change the world.They were not a politician, a general, or a celebrity.They were just a teenager. And yet with one small act, they ignited a spark that would fuel a global movement, topple regimes, or shift the course of history. This is the story of how one teenager, often by accident, became the unlikely catalyst of revolution.And why it proves that even the smallest voice can create the loudest echoes. The Real-Life Story: Mohamed Bouazizi and the Arab Spring On December 17, 2010, in the small Tunisian town of Sidi Bouzid, Mohamed Bouazizi, a 26-year-old street vendor (not technically a teen, but still a young adult), had had enough. Harassed by local officials, humiliated in public, and desperate to survive, he set himself on fire outside the local governor’s office. It was an act of protest.It was also a cry for dignity. No one not even Bouazizi could have predicted what came next. His self-immolation triggered mass protests in Tunisia, which soon spiraled into a nationwide uprising…..and then across borders into Egypt, Libya, Syria, Yemen, and beyond. That one act the result of long-felt frustration sparked the Arab Spring, a sweeping revolutionary wave that shook the Middle East and North Africa, toppled authoritarian leaders, and reshaped geopolitics. But What About Actual Teenagers? History has many examples of teenagers whose courage intentional or accidentally lit the fire of rebellion: 1. Gavrilo Princip (Age 19) – The Teen Who Triggered WWI In 1914, Gavrilo Princip, a 19-year-old Bosnian Serb nationalist, shot Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.He thought he was striking a blow for independence. Instead, his bullets set off a chain reaction of alliances, declarations of war, and political chaos that led to World War I, resulting in over 16 million deaths and the complete redrawing of global borders. One teenager. One moment. A century forever altered. 2. Malala Yousafzai (Age 15) The Teen Who Stood Up for Girls’ Education In 2012, Malala, a Pakistani schoolgirl, was shot in the head by the Taliban for advocating girls’ education.She survived. Instead of staying silent, she spoke louder than ever, becoming a global symbol of resistance against extremism.By 17, she was the youngest-ever Nobel Peace Prize laureate. Her fight became a revolution in its own right for education, rights, and resilience. 3. Claudette Colvin (Age 15) – Before Rosa Parks, There Was Claudette Nine months before Rosa Parks famously refused to give up her seat, Claudette Colvin, a 15-year-old Black schoolgirl in Montgomery, Alabama, did the same.She was dragged off the bus and arrested. Though history later credited Parks as the spark of the Civil Rights Movement, Colvin’s act helped set it in motion and challenged segregation at its core. Sometimes revolutions begin with forgotten names and quiet bravery. 4. Greta Thunberg (Age 15) Skipping School to Save the Planet In 2018, a Swedish teenager named Greta Thunberg started skipping school to protest climate inaction outside parliament. It started as a solo demonstration.It became Fridays for Future, a global youth-led movement involving millions. Greta didn’t plan to lead a revolution she just refused to sit still. What These Stories Prove You don’t need power, wealth, or a microphone to make history.All you need is: Conviction Courage And sometimes…..a moment that catches fire Revolutions don’t always begin with battle cries.Sometimes they begin with a whisper, a refusal, or a desperate act of truth. Did You Know? Over 60% of revolutionary movements in the past 50 years involved students or youth at the core. Social media has made it easier than ever for one voice to spark global protest. In psychology, this is called the “butterfly effect” a small action in one place can lead to massive consequences elsewhere. The Takeaway A teenager with a sign.A student with a voice.A young person who says “no.” That is all it takes sometimes to tip a nation, to start a movement, or to change the future. So when someone says, “You are just a kid”…Remember:That might be your superpower.
The Robot That Smells-And Why It’s a Big Deal
Robots are now learning to smell and it is more important than you think. Discover how the first scent-detecting robot is changing everything from medicine to national security. The First Robot That Can Smell Here is Why That Matters We have seen robots that can walk, talk, learn, and even recognize faces.But now, scientists have achieved something almost no one expected: They have built a robot that can smell. Yes, smell.Like detect odors whether it is a dangerous gas leak or the aroma of freshly baked bread. It might sound like a novelty, but this breakthrough is a giant leap in robotics, with mind-blowing implications for health, safety, environmental monitoring, and even space exploration. Let’s dive into how this works and why it matters more than you think. Meet the “Smelling Robot” In recent years, researchers from Tel Aviv University (Israel), MIT (USA), and other leading institutions have developed bio-hybrid robots capable of scent detection. One such robot was equipped with a biological olfactory system not just sensors, but actual insect antennae, harvested from locusts or fruit flies. These antennae are wired to the robot’s processing unit, allowing it to detect smells in real-time. Another variant uses artificial intelligence paired with chemical sensors that mimic how a human nose identifies scent molecules. The result? A robot that can “smell” chemicals 10,000 times more sensitively than current gas detectors. How Does It Work? There are two main approaches: 1. Biohybrid Olfaction Uses real biological tissue (like insect antennae or mammalian receptors) Connects to neural processors or electrodes Translates chemical signals into data 2. Electronic Nose (eNose) Uses arrays of gas sensors Combined with machine learning to “learn” smells over time Can differentiate between complex odor patterns like wine, smoke, or disease markers These robots don’t just detect scents they analyze and interpret them like a real nose connected to a brain. Why This Changes Everything Smelling robots could revolutionize multiple industries. Here’s how: 1. Medical Diagnosis Some diseases give off specific chemical markers. For example: Parkinson’s disease can be detected by scent before symptoms appear Lung or breast cancer releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in breath Robots could sniff out illness in seconds noninvasively Imagine walking into a clinic, and instead of a blood test, you just breathe, and the robot diagnoses you. 2. Disaster Response Smelling robots could detect: Gas leaks before explosions Toxic chemicals in war zones Trapped humans under rubble by the CO₂ or sweat they release They could operate in dangerous or contaminated environments where human noses would fail. 3. Environmental Monitoring Robots could monitor air quality and pollution at: Factories Landfills Farms (to detect methane or ammonia) And report back real-time, accurate chemical data. 4. Security & Anti-Terrorism Traditional scanners can not always detect: Explosives Illegal drugs Chemical weapons But scent-trained robots could become super-sniffers in airports and border patrols far more reliable than sniffer dogs. 5. Space Exploration On other planets, a robot that can smell could: Detect alien gases Smell for signs of biological activity Evaluate air quality in a space station NASA has already invested in “e-nose” tech for use aboard the International Space Station. Did You Know? The human nose can detect over 1 trillion different scents Some animals, like dogs and moths, can detect certain chemicals at parts per trillion New AI “e-noses” are already being trained to identify cancers, Covid-19, and even emotion-based pheromones The Takeaway Smell is one of the most ancient and complex senses, yet we are only now giving robots the ability to use it. It is not just about making machines more human it is about amplifying their potential to keep us safe, healthy, and one step ahead. A robot that can smell is not just science fiction anymore.It is the nose of the future and it is already sniffing out the next big breakthrough.
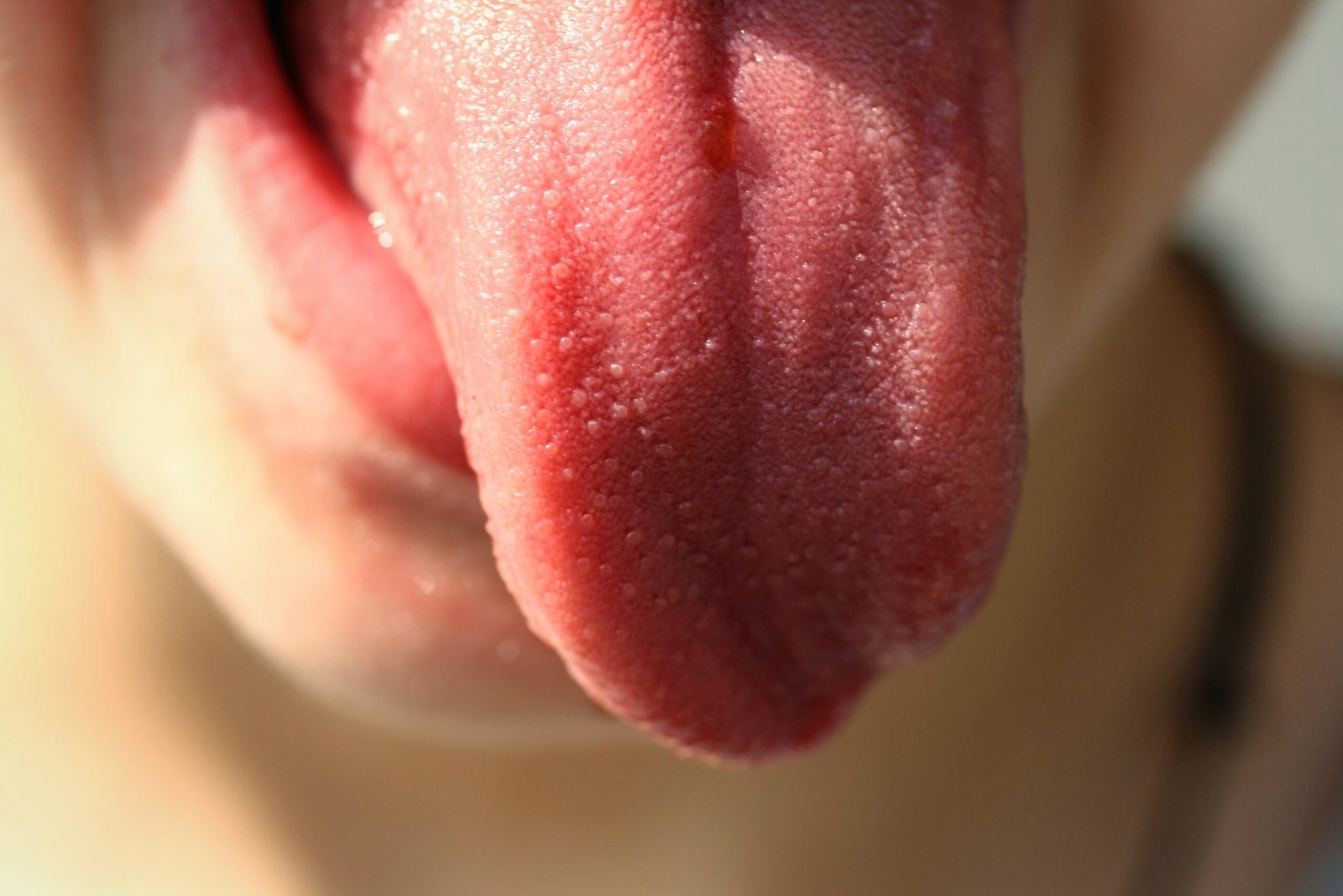
7 Strange Things Your Tongue Says About Your Health
Your tongue may be silently trying to tell you something about your health. Discover what color, coating, texture, or bumps on your tongue could reveal about your digestion, hydration, and even disease. What Your Tongue Can Reveal About Your Health Stuck your tongue out lately? No, not for a selfie but to actually look at it? That small pink muscle in your mouth may be one of the most underestimated diagnostic tools your body has. Doctors across cultures from Western medicine to ancient Chinese healing have long used the tongue as a mirror of internal health. So before you brush it off (literally), here is how your tongue could be revealing hidden clues about your hydration, nutrition, immune function, or even disease. Why Your Tongue Is a Health Barometer Your tongue is a muscular organ covered in thousands of papillae (tiny bumps) and taste buds.It also has a rich blood supply, and its surface reflects changes in your: Circulation Digestive health Immune response Nutritional status Hormonal balance Subtle changes in color, texture, coating, or shape can be your body’s early warning system. Let us decode the signs: 1. Red or Bright Red Tongue What it may mean: Vitamin deficiencies, especially B12, folic acid, or iron Fever or infection Geographic tongue (harmless but irregular patches) If your tongue feels smooth and red, it might signal anemia or inflammation. 2. Pale or White Tongue What it may mean: Anemia or poor circulation Dehydration Oral thrush (a yeast infection, especially if the white coating is thick) Cold or weakened immune system (in Traditional Chinese Medicine) Tip: Increase water intake and check iron levels if persistent. 3. Yellow Coating What it may mean: Digestive imbalance Excess bacteria buildup Liver or gallbladder issues Smoking or poor oral hygiene A yellow film is often related to microbial overgrowth or internal “heat” conditions in Eastern medicine. 4. Black or Brown Tongue What it may mean: Poor oral hygiene Use of antibiotics or certain medications Smoking or chewing tobacco Overgrowth of bacteria or fungi (aka “black hairy tongue”) Although alarming, it is often harmless and fixable with better oral care and diet adjustments. 5. Bumps, Sores, or Ulcers What it may mean: Canker sores or viral infections Stress, food sensitivities, or hormonal shifts In rare cases: oral cancer (if bumps don’t heal in 2+ weeks) Recurrent or painful sores deserve medical attention. 6. Thick White Coating What it may mean: Candida (oral thrush) Poor digestion or toxin buildup Chronic dehydration Try gently brushing your tongue and drinking more water if it persists, consult a doctor. 7. Scalloped Edges or Teeth Marks What it may mean: Water retention Sleep apnea or tongue swelling Jaw clenching (bruxism) In TCM: spleen qi deficiency (fatigue, bloating) Look in the mirror do the sides of your tongue look “wavy”? That is scalloping, and it might signal underlying tension or inflammation. 8. Smooth or Shiny Tongue What it may mean: Nutritional deficiencies (B-complex vitamins, iron) Hormonal changes Autoimmune conditions A smooth tongue may appear healthy, but if it’s sore or tender, something deeper might be going on. When to See a Doctor Consult a professional if you notice: Persistent pain or color changes Bumps or ulcers that last more than 2 weeks Bleeding without injury Thick coatings that don’t go away A sudden change in taste or texture The Tongue in Traditional Medicine In Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the tongue is a map of the organs. For example: Tongue Area Linked Organ (TCM) Tip Heart & lungs Sides Liver & gallbladder Center Stomach & spleen Back Kidneys & intestines Practitioners use tongue observation for early disease detection, especially when lab tests are inaccessible. Did You Know? Your tongue can regenerate taste buds every 10–14 days Dehydration is one of the top causes of a coated tongue Over 700 different bacterial species can live in your mouth Oral signs often appear before systemic illness becomes obvious The Takeaway Your tongue is more than a taste tester it is a health indicator. From nutrient deficiencies to infections and immune imbalance, it may be quietly pointing you toward what your body needs before symptoms even show up. So the next time you brush your teeth, take an extra second to check your tongue.It might just be the health checkup you didn’t know you needed.
Top 9 Weird Laws That Still Exist in 2025
Think all laws make sense? Think again. From banning ice cream in your back pocket to outlawing high heels in historic zones, these bizarre laws are still in effect in 2025 and #4 will leave you speechless. Weirdest Laws Still in Effect in 2025 You Won’t Believe #4 You would think by now most outdated or bizarre laws would have been repealed.But no across the world (and even in the U.S.), there are still laws on the books that sound more like a joke than real legislation. Some are ancient relics that were never removed.Others were passed for oddly specific reasons.And a few? They might even make some twisted kind of sense. Here are the weirdest laws that are STILL legally enforceable in 2025 and yes, #4 is 100% real. 1. It is Illegal to Wear High Heels at Greek Historic Sites (Greece) Planning to strut through the Parthenon in stilettos? Think again. Since 2009, Greece has banned high heels at ancient monuments to prevent damage to fragile stone surfaces. Why? Sharp heels can chip away centuries-old marble.So keep it flat if you want to see the ruins fashion has limits. 2. No Ice Cream in Your Back Pocket on Sundays (Alabama, USA) Wait, what? This old Southern law was reportedly designed to stop horse theft in the 1800s.Thieves would place ice cream in their back pocket, and horses tempted by the scent would follow them away without technically being “stolen.” It may sound silly, but it is still technically on the books in parts of Alabama and Georgia. 3. It is Illegal to Die in Parliament (United Kingdom) This famous UK law is so strange it is often assumed to be a myth.But it is real though symbolic. According to tradition, dying in the Houses of Parliament qualifies you for a state funeral, so the law was meant to prevent complications by forbidding it outright. Obviously unenforceable (you can not punish the dead), but still a hilarious legal oddity. 4. It is Illegal to Take More Than One Shower a Day (California, USA drought-prone zones) Yes, really. Some municipalities in California, especially during drought declarations, have laws limiting water usage, including how many times residents can legally shower per day. In some cities, violations can lead to fines if they exceed 55 gallons of water per person per day which includes laundry, toilets, AND bathing. Want a second rinse? You might technically be breaking the law. 5. No Chewing Gum Allowed (Singapore) This one’s legendary and still enforced. Singapore strictly prohibits the import and sale of chewing gum, except for therapeutic dental or nicotine gums prescribed by a doctor. Why? To keep streets clean and subways gum-free.Littering with gum can cost you hundreds in fines, and repeat offenders might face mandatory community cleaning. 6. Couples Must Not Sleep Naked on Train Roofs (India) While this sounds like satire, it originates from obscure railway regulations aimed at maintaining “public decency” in rural areas with open-roof sleeper trains. While such behavior is rare (and probably uncomfortable), the law technically bans it. 7. Chickens Can not Cross the Road in Quitman, Georgia (USA) In this little Georgia town, poultry owners are responsible for keeping chickens off the roads. Why?To prevent traffic hazards and preserve the mystery of why the chicken crossed the road in the first place 8. It is Illegal to Own More Than 110 Pounds of Video Games (Switzerland) Some Swiss cantons have weight-based storage laws (yes, weight, not file size) for electronic and digital goods.The law originated to prevent overloading residential power grids with too many power-consuming devices. While rarely enforced today, technically owning a massive retro game collection could land you in hot water. 9. You Can not Frown at a Police Dog (Italy) In Turin, Italy, the law requires respectful treatment of pets and working animals.Offending a police dog especially during duty can result in fines or charges under animal protection laws. So yes, technically, frowning at a K-9 can be interpreted as “intimidation” or “provocation.” 10. It is Illegal to Forget Your Wife’s Birthday (Samoa) In Samoa, forgetting your spouse’s birthday is more than just a marital mistake it is a punishable offense. While the law is loosely enforced, local courts can and have issued fines or mandated public apologies in domestic disputes involving “neglect.” So…..maybe set that calendar reminder. The Takeaway From the hilarious to the head-scratching, these bizarre laws show us that legal systems are far from perfect or always rational. Some were written for reasons long forgotten.Others reflect unique cultural values or historical quirks.And a few? They still matter more than you’d think. Next time you travel or debate a weird rule, remember:What seems absurd today might have been dead serious 100 years ago.